Tesla Space Drive
| This article may require cleanup to meet our quality standards. The specific problem is: Information needs to be compiled and cleaned up. |
Source: http://fuel-efficient-vehicles.org/energy-news/?page_id=1284
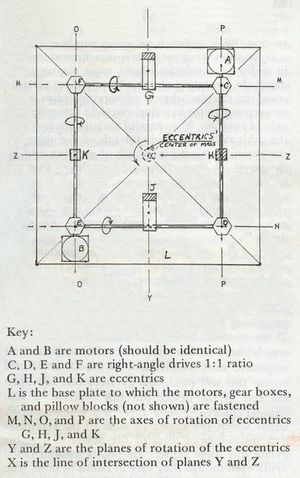
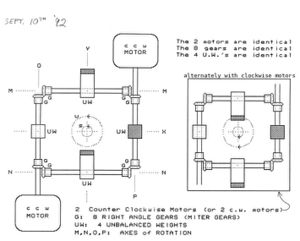
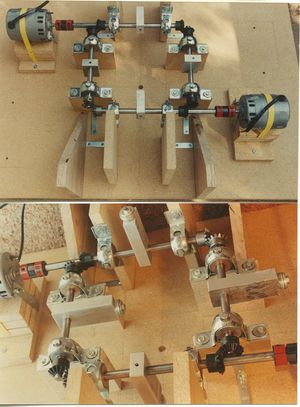
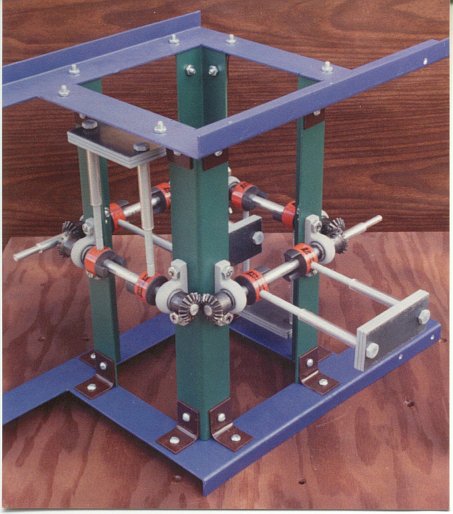
The Tesla Space Drive, also known as the flying stove and Tesla Flying Machine, is a reactionless drive invented by Nikola Tesla utilizing gyroscopic principles. Its basic construction is four counter-balances arranged in a square, each made to rotate inwards out of phase. The proposed effect is a net force in the axis of the center of the square according to the right-hand rule. It should wobble at low thrust levels due to the noncontinuous nature of its motion which will fade as the thrust is increased.
The effect is suggested to be caused by circular acceleration of the drive's center of mass with no centripetal force, causing forward linear acceleration. This is comparable to electrons flowing in a coil, where the "mass" is rotating around a central axis but the frame itself is stationary, causing a forward linear force on ferromagnetic materials.